
| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
You can set and query graphics object properties in two ways:
set and get commands enable you to set and query the values of propertiesTo change the default value of properties see Settingcreating_plots Default Property Values.
Text Property Descriptions
This section lists property names along with the types of values each accepts. Curly braces { } enclose default values.
BusyAction cancel | {queue}
Callback routine interruption. The BusyAction property enables you to control how MATLAB handles events that potentially interrupt executing callback routines. If there is a callback routine executing, subsequently invoked callback routines always attempt to interrupt it. If the Interruptible property of the object whose callback is executing is set to on (the default), then interruption occurs at the next point where the event queue is processed. If the Interruptible property is off, the BusyAction property (of the object owning the executing callback) determines how MATLAB handles the event. The choices are:
cancel - discard the event that attempted to execute a second callback routine.queue - queue the event that attempted to execute a second callback routine until the current callback finishes.ButtonDownFcn string
Button press callback routine. A callback routine that executes whenever you press a mouse button while the pointer is over the text object. Define this routine as a string that is a valid MATLAB expression or the name of an M-file. The expression executes in the MATLAB workspace.
Children matrix (read only)
The empty matrix; text objects have no children.
Clipping on | {off}
Clipping mode. When Clipping is on, MATLAB does not display any portion of the text that is outside the axes.
Color ColorSpec
Text color. A three-element RGB vector or one of MATLAB 's predefined names, specifying the text color. The default value for Color is white. See ColorSpec for more information on specifying color.
CreateFcn string
Callback routine executed during object creation. This property defines a callback routine that executes when MATLAB creates a text object. You must define this property as a default value for text. For example, the statement,
set(0,'DefaultTextCreateFcn',... 'set(gcf,''Pointer'',''crosshair'')')
defines a default value on the root level that sets the figure Pointer property to a crosshair whenever you create a text object. MATLAB executes this routine after setting all text properties. Setting this property on an existing text object has no effect.
The handle of the object whose CreateFcn is being executed is accessible only through the root CallbackObject property, which you can query using gcbo.
DeleteFcn string
Delete text callback routine. A callback routine that executes when you delete the text object (e.g., when you issue a delete command or clear the axes or figure). MATLAB executes the routine before destroying the object's properties so these values are available to the callback routine.
The handle of the object whose DeleteFcn is being executed is accessible only through the root CallbackObject property, which you can query using gcbo.
Editing on | {off}
Enable or disable editing mode. When this property is set to the default off, you cannot edit the text string interactively (i.e., you must change the String property to change the text). When this property is set to on, MATLAB places an insert cursor at the beginning of the text string and enables editing. To apply the new text string:
Editing property to offMATLAB then updates the String property to contain the new text and resets the Editing property to off. You must reset the Editing property to on to again resume editing.
EraseMode {normal} | none | xor | background
Erase mode. This property controls the technique MATLAB uses to draw and erase text objects. Alternative erase modes are useful for creating animated sequences, where controlling the way individual object redraw is necessary to improve performance and obtain the desired effect.
normal -- Redraw the affected region of the display, performing the three-dimensional analysis necessary to ensure that all objects are rendered correctly. This mode produces the most accurate picture, but is the slowest. The other modes are faster, but do not perform a complete redraw and are therefore less accurate.none -- Do not erase the text when it is moved or destroyed. While the object is still visible on the screen after erasing with EraseMode none, you cannot print it because MATLAB stores no information about its former location.xor -- Draw and erase the text by performing an exclusive OR (XOR) with each pixel index of the screen beneath it. When the text is erased, it does not damage the objects beneath it. However, when text is drawn in xor mode, its color depends on the color of the screen beneath it and is correctly colored only when over axes background Color, or the figure background Color if the axes Color is set to none.background -- Erase the text by drawing it in the background Color, or the figure background Color if the axes Color is set to none. This damages objects that are behind the erased text, but text is always properly colored.MATLAB always prints figures as if the EraseMode of all objects is normal. This means graphics objects created with EraseMode set to none, xor, or background can look different on screen than on paper. On screen, MATLAB may mathematically combine layers of colors (e.g., XORing a pixel color with that of the pixel behind it) and ignore three-dimensional sorting to obtain greater rendering speed. However, these techniques are not applied to the printed output.
You can use the MATLAB getframe command or other screen capture application to create an image of a figure containing non-normal mode objects.
Extent position rectangle (read only)
Position and size of text. A four-element read-only vector that defines the size and position of the text string.
[left,bottom,width,height]
If the Units property is set to data (the default), left and bottom are the x and y coordinates of the lower-left corner of the text Extent rectangle.
For all other values of Units, left and bottom are the distance from the lower-left corner of the axes position rectangle to the lower-left corner of the text Extent rectangle. width and height are the dimensions of the Extent rectangle. All measurements are in units specified by the Units property.
FontAngle {normal} | italic | oblique
Character slant. MATLAB uses this property to select a font from those available on your particular system. Generally, setting this property to italic or oblique selects a slanted font.
FontName A name such as Courier or the string FixedWidth
Font family. A string specifying the name of the font to use for the text object. To display and print properly, this must be a font that your system supports. The default font is Helvetica.
Specifying a Fixed-Width Font
If you want text to use a fixed-width font that looks good in any locale, you should set FontName to the string FixedWidth:
set(text_handle,'FontName','FixedWidth')
This eliminates the need to hardcode the name of a fixed-width font, which may not display text properly on systems that do not use ASCII character encoding (such as in Japan where multibyte character sets are used). A properly written MATLAB application that needs to use a fixed-width font should set FontName to FixedWidth (note that this string is case sensitive) and rely on FixedWidthFontName to be set correctly in the end-user's environment.
End users can adapt a MATLAB application to different locales or personal environments by setting the root FixedWidthFontName property to the appropriate value for that locale from startup.m.
Note that setting the root FixedWidthFontName property causes an immediate update of the display to use the new font.
FontSize size in FontUnits
Font size. An integer specifying the font size to use for text, in units determined by the FontUnits property. The default point size is 10 (1 point = 1/72 inch).
FontWeight light | {normal} | demi | bold
Weight of text characters. MATLAB uses this property to select a font from those available on your particular system. Generally, setting this property to bold or demi causes MATLAB to use a bold font.
FontUnits {points} | normalized | inches |
centimeters | pixels
Font size units. MATLAB uses this property to determine the units used by the FontSize property. Normalized units interpret FontSize as a fraction of the height of the parent axes. When you resize the axes, MATLAB modifies the screen FontSize accordingly. pixels, inches, centimeters, and points are absolute units (1 point = 1/72 inch).
HandleVisibility {on} | callback | off
Control access to object's handle by command-line users and GUIs. This property determines when an object's handle is visible in its parent's list of children. HandleVisibility is useful for preventing command-line users from accidentally drawing into or deleting a figure that contains only user interface devices (such as a dialog box).
Handles are always visible when HandleVisibility is on.
Setting HandleVisibility to callback causes handles to be visible from within callback routines or functions invoked by callback routines, but not from within functions invoked from the command line. This provides a means to protect GUIs from command-line users, while allowing callback routines to have complete access to object handles.
Setting HandleVisibility to off makes handles invisible at all times. This may be necessary when a callback routine invokes a function that might potentially damage the GUI (such as evaluating a user-typed string), and so temporarily hides its own handles during the execution of that function.
When a handle is not visible in its parent's list of children, it cannot be returned by functions that obtain handles by searching the object hierarchy or querying handle properties. This includes get, findobj, gca, gcf, gco, newplot, cla, clf, and close.
When a handle's visibility is restricted using callback or off, the object's handle does not appear in its parent's Children property, figures do not appear in the root's CurrentFigure property, objects do not appear in the root's CallbackObject property or in the figure's CurrentObject property, and axes do not appear in their parent's CurrentAxes property.
You can set the root ShowHiddenHandles property to on to make all handles visible, regardless of their HandleVisibility settings (this does not affect the values of the HandleVisibility properties).
Handles that are hidden are still valid. If you know an object's handle, you can set and get its properties, and pass it to any function that operates on handles.
HitTest {on} | off
Selectable by mouse click. HitTest determines if the text can become the current object (as returned by the gco command and the figure CurrentObject property) as a result of a mouse click on the text. If HitTest is off, clicking on the text selects the object below it (which is usually the axes containing it).
For example, suppose you define the button down function of an image (see the ButtonDownFcn property) to display text at the location you click on with the mouse.
First define the callback routine.
function bd_function
pt = get(gca,'CurrentPoint');
text(pt(1,1),pt(1,2),pt(1,3),...
'{\fontsize{20}\oplus} The spot to label',...
'HitTest','off')
Now display an image, setting its ButtonDownFcn property to the callback routine.
load earth image(X,'ButtonDownFcn','bd_function'); colormap(map)
When you click on the image, MATLAB displays the text string at that location. With HitTest set to off, existing text cannot intercept any subsequent button down events that occur over the text. This enables the image's button down function to execute.
HorizontalAlignment {left} | center | right
Horizontal alignment of text. This property specifies the horizontal justification of the text string. It determines where MATLAB places the string with regard to the point specified by the Position property. The following picture illustrates the alignment options.

See the Extent property for related information.
Interpreter {tex} | none
Interpret Tex instructions. This property controls whether MATLAB interprets certain characters in the String property as Tex instructions (default) or displays all characters literally. See the String property for a list of support Tex instructions.
Interruptible {on} | off
Callback routine interruption mode. The Interruptible property controls whether a text callback routine can be interrupted by subsequently invoked callback routines. text objects have four properties that define callback routines: ButtonDownFcn, CreateFcn, and DeleteFcn. See the BusyAction property for information on how MATLAB executes callback routines.
Parent handle
Text object's parent. The handle of the text object's parent object. The parent of a text object is the axes in which it is displayed. You can move a text object to another axes by setting this property to the handle of the new parent.
Position [x,y,[z]]
Location of text. A two- or three-element vector, [x y [z]], that specifies the location of the text in three dimensions. If you omit the z value, it defaults to 0. All measurements are in units specified by the Units property. Initial value is [0 0 0].
Rotation scalar (default = 0)
Text orientation. This property determines the orientation of the text string. Specify values of rotation in degrees (positive angles cause counterclockwise rotation).
Selected on | {off}
Is object selected? When this property is on, MATLAB displays selection handles if the SelectionHighlight property is also on. You can, for example, define the ButtonDownFcn to set this property, allowing users to select the object with the mouse.
SelectionHighlight {on} | off
Objects highlight when selected. When the Selected property is on, MATLAB indicates the selected state by drawing four edge handles and four corner handles. When SelectionHighlight is off, MATLAB does not draw the handles.
String string
The text string. Specify this property as a quoted string for single-line strings, or as a cell array of strings or a padded string matrix for multiline strings. MATLAB displays this string at the specified location. Vertical slash characters are not interpreted as linebreaks in text strings, and are drawn as part of the text string. See the "Remarks" section for more information.
When the text Interpreter property is Tex (the default), you can use a subset of TeX commands embedded in the string to produce special characters such as Greek letters and mathematical symbols. The following table lists these characters and the character sequence used to define them.
You can also specify stream modifiers that control the font used. The first four modifiers are mutually exclusive. However, you can use \fontname in combination with one of the other modifiers:
\bf - bold font\it - italics font\sl - oblique font (rarely available)\rm - normal font\fontname{fontname} - specify the name of the font family to use.\fontsize{fontsize} - specify the font size in FontUnits.Stream modifiers remain in effect until the end of the string or only within the context defined by braces { }.
Specifying Subscript and Superscript Characters
The subscript character "_" and the superscript character "^" modify the character or substring defined in braces immediately following.
To print the special characters used to define the Tex strings when Interpreter is Tex, prefix them with the backslash "\" character: \\, \{, \} \_, \^.
See the example for more information.
When Interpreter is none, no characters in the String are interpreted, and all are displayed when the text is drawn.
Tag string
User-specified object label. The Tag property provides a means to identify graphics objects with a user-specified label. This is particularly useful when constructing interactive graphics programs that would otherwise need to define object handles as global variables or pass them as arguments between callback routines. You can define Tag as any string.
Type string (read only)
Class of graphics object. For text objects, Type is always the string 'text'.
Units pixels | normalized | inches |
centimeters | points | {data}
Units of measurement. This property specifies the units MATLAB uses to interpret the Extent and Position properties. All units are measured from the lower-left corner of the axes plotbox. Normalized units map the lower-left corner of the rectangle defined by the axes to (0,0) and the upper-right corner to (1.0,1.0). pixels, inches, centimeters, and points are absolute units (1 point = 1/72 inch). data refers to the data units of the parent axes.
If you change the value of Units, it is good practice to return it to its default value after completing your computation so as not to affect other functions that assume Units is set to the default value.
UserData matrix
User-specified data. Any data you want to associate with the text object. MATLAB does not use this data, but you can access it using set and get.
UIContextMenu handle of a uicontextmenu object
Associate a context menu with the text. Assign this property the handle of a uicontextmenu object created in the same figure as the text. Use the uicontextmenu function to create the context menu. MATLAB displays the context menu whenever you right-click over the text.
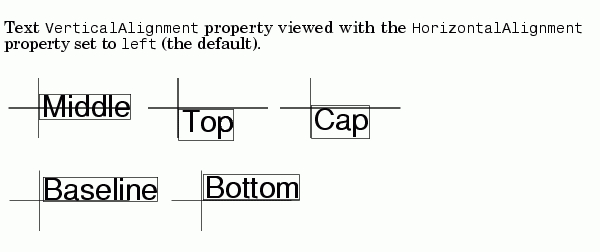
VerticalAlignment top | cap | {middle} | baseline |
bottom
Vertical alignment of text. This property specifies the vertical justification of the text string. It determines where MATLAB places the string with regard to the value of the Position property. The possible values mean:
top - Place the top of the string's Extent rectangle at the specified y-position.cap - Place the string so that the top of a capital letter is at the specified y-position.middle - Place the middle of the string at specified y-position.baseline - Place font baseline at the specified y-position.bottom - Place the bottom of the string's Extent rectangle at the specified y-position.The following picture illustrates the alignment options.
Visible {on} | off
Text visibility. By default, all text is visible. When set to off, the text is not visible, but still exists and you can query and set its properties.
 | text | textread |  |