
| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Creates a 3-D stream ribbon plot
Syntax
streamribbon(X,Y,Z,U,V,W,startx,starty,startz) streamribbon(U,V,W,startx,starty,startz) streamribbon(vertices,X,Y,Z,cav,speed) streamribbon(vertices,cav,speed) streamribbon(vertices,twistangle) streamribbon(...,width) h = streamribbon(...)
Description
streamribbon(X,Y,Z,U,V,W,startx,starty,startz)
draws stream ribbons from vector volume data U, V, W. The arrays X, Y, Z define the coordinates for U, V, W and must be monotonic and 3-D plaid (as if produced by meshgrid). startx, starty, and startz define the starting positions of the stream ribbons at the center of the ribbons. The section Starting Points for Stream Plots in Visualization Techniques provides more information on defining starting points.
The twist of the ribbons is proportional to the curl of the vector field. The width of the ribbons is calculated automatically.
Generally, you should set the DataAspectRatio (daspect) before calling streamribbon.
streamribbon(U,V,W,startx,starty,startz) assumes
X, Y, and Z are determined by the expression:
[X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(1:n,1:m,1:p)
streamribbon(vertices,X,Y,Z,cav,speed) assumes precomputed streamline vertices, curl angular velocity, and flow speed.
vertices is a cell array of stream line vertices (as produced by stream3). X, Y, Z, cav, and speed are 3-D arrays.
streamribbon(vertices,cav,speed) assumes
X, Y, and Z are determined by the expression:
[X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(1:n,1:m,1:p)
streamribbon(vertices,twistangle)
uses the cell array of vectors twistangle for the twist of the ribbons (in radians). The size of each corresponding element of vertices and twistangle must be equal.
streamribbon(...,width)
sets the width of the ribbons to width.
h = streamribbon(...)
returns a vector of handles (one per start point) to surface objects.
Examples
This example uses stream ribbons to indicate the flow in the wind data set. Inputs include the coordinates, vector field components, and starting location for the stream ribbons.
load wind [sx sy sz] = meshgrid(80,20:10:50,0:5:15); daspect([1 1 1]) streamribbon(x,y,z,u,v,w,sx,sy,sz); %-----Define viewing and lighting axis tight shading interp; view(3); camlight; lighting gouraud
This example uses precalculated vertex data (stream3), curl average velocity (curl), and speed (
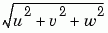 ). Using precalculated data enables you to use values other than those calculated from the single data source. In this case, the speed is reduced by a factor of 10 compared to the previous example.
). Using precalculated data enables you to use values other than those calculated from the single data source. In this case, the speed is reduced by a factor of 10 compared to the previous example.
load wind [sx sy sz] = meshgrid(80,20:10:50,0:5:15); daspect([1 1 1]) verts = stream3(x,y,z,u,v,w,sx,sy,sz); cav = curl(x,y,z,u,v,w); spd = sqrt(u.^2 + v.^2 + w.^2).*.1; streamribbon(verts,x,y,z,cav,spd); %-----Define viewing and lighting axis tight shading interp view(3) camlight; lighting gouraud
This example specifies a twist angle for the stream ribbon.
t = 0:.15:15;
verts = {[cos(t)' sin(t)' (t/3)']};
twistangle = {cos(t)'};
daspect([1 1 1])
streamribbon(verts,twistangle);
%-----Define viewing and lighting
axis tight
shading interp;
view(3);
camlight; lighting gouraud
This example combines cone plots (coneplot) and stream ribbon plots in one graph.
%-----Define 3-D arrays x, y, z, u, v, w
xmin = -7; xmax = 7;
ymin = -7; ymax = 7;
zmin = -7; zmax = 7;
x = linspace(xmin,xmax,30);
y = linspace(ymin,ymax,20);
z = linspace(zmin,zmax,20);
[x y z] = meshgrid(x,y,z);
u = y; v = -x; w = 0*x+1;
daspect([1 1 1]);
[cx cy cz] = meshgrid(linspace(xmin,xmax,30),...
linspace(ymin,ymax,30),[-3 4]);
h = coneplot(x,y,z,u,v,w,cx,cy,cz,'quiver');
set(h,'color','k');
%-----Plot two sets of streamribbons
[sx sy sz] = meshgrid([-1 0 1],[-1 0 1],-6);
streamribbon(x,y,z,u,v,w,sx,sy,sz);
[sx sy sz] = meshgrid([1:6],[0],-6);
streamribbon(x,y,z,u,v,w,sx,sy,sz);
%-----Define viewing and lighting
shading interp
view(-30,10) ; axis off tight
camproj perspective; camva(66); camlookat;
camdolly(0,0,.5,'fixtarget')
camlight
See also
curl, streamtube, streamline, stream3
 | streamparticles | streamslice |  |