When we analyze audio signals, we usually adopt the method of short-term analysis since most audio signals are more or less stable within a short period of time, say 20 ms or so. When we do frame blocking, there may be some soverlap between neighboring frames to capture subtle change in the audio signals. Note that each frame is the basic unit for our analysis. Within each frame, we can observe the three most distinct acoustic features, as follows.
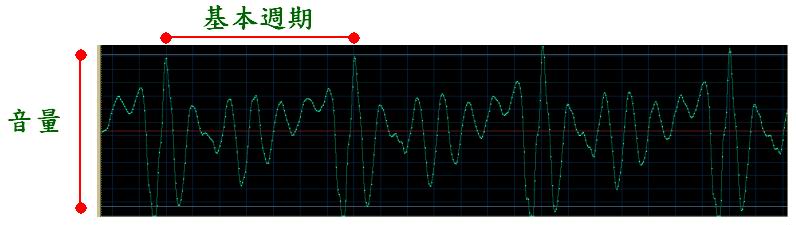
- Volume: This feature represents the loudness of the audio signal, which is correlated to the amplitude of the signals. Sometimes it is also referred to as energy or intensity of audio signals.
- Pitch: This feature represents the vibration rate of audio signals, which can be represented by the fundamental frequency, or equivalently, the reciprocal of the fundamental period of voiced audio signals.
- Timbre: This feature represents the meaningful content (such as a vowel in English) of audio signals, which is characterized by the waveform within a fundamental period of voice signals.
Take human voices as an example, then the above three acoustic features will correlates to some physical quantities:
- Volume: It correlates to the compression of your lungs. A large volume of audio signals corresponds to a large compression.
- Pitch: It correlates to the vibration frequency of your vocal cord. A high pitch corresponds to a high vibration frequency.
- Timbre: It correlates to the positions and shapes of your lips and tongue. Different timbres corresponds to different positions and shapes of your lips and tongue.
We shall explain methods to extract these acoustic features in the other chapters of this book. It should be noted that these acoustic features mostly corresponds to human's "perception" and therefore cannot be represented exactly by mathematical formula or quantities. However, we still try to "quantitify" these features for further computer-based analysis in the hope that the used formula or quantities can emulate human's perception as closely as possible.
The basic approach to the extraction of audio acoustic features can be summarized as follows:
- Perform frame blocking such that a strem of audio signals is converted to a set of frames. The time duration of each frame is about 20~30 ms. If the frame duration is too big, we cannot catch the time-varying characteristics of the audio signals. On the other hand, if the frame duration is too small, then we cannot extract valid acoustic features. In general, a frame should be contains several fundamental periods of the given audio signals. Usually the frame size (in terms of sample points) is equal to the powers of 2 (such as 256, 512, 1024 ,etc) such that it is suitable for fast fourier transform.
- If we want to reduce the difference between neighboring frames, we can allow overlap between them. Usually the overlap is 1/2 to 2/3 of the original frame. The more overlap, the more computation is needed.
- Assuming the audio signals within a frame is stationary, we can extract acoustic features such as zero crossing rates, volume, pitch, MFCC, LPC, etc.
- We can perform endpoint detection based on zero crossing rate and volume, and keep non-silence frames for further analysis.
When we are performing the above procedures, there are several terminologies that are used often:
- Frame size: The sampling points within each frame
- Frame overlap: The sampling points of the overlap between consecutive frames
- Frame step (or hop size): This is equal to the frame size minus the overlap.
- Frame rate: The number of frames per second, which is equal to the sample frequency divided by the frame step.
For instance, if we have a stream of audio signals with sample frequency fs=16000, and a frame duration of 25 ms, overlap of 15 ms, then
- Frame size = fs*25/1000 = 400 (sample points)。
- Frame overlap = fs*15/1000 = 240 (sample points)。
- Frame step (or hop size) = 400-240 = 160 (sample points)。
- Frame rate = fs/160 = 100 frames/sec。
Audio Signal Processing and Recognition (音訊處理與辨識)
